The Chinese call their country ZhongGuó (pronounced joong gwo) or Middle Kingdom. In simplified Chinese, it is written as:
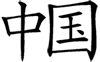
The origin of the second character gives insight as to what was important in the culture.
 This is the symbol for the emperor
This is the symbol for the emperor
 Give him something precious to hold and this symbol becomes 'jade'
Give him something precious to hold and this symbol becomes 'jade'
 Put a wall around them to keep them safe and it becomes a kingdom
Put a wall around them to keep them safe and it becomes a kingdom
The country's official name changed with each dynasty. The name "ZhongGuo" first appeared in the 6th century BC and referred to the Western Zhou Dynasty, who believed they were the 'center of civilization.' It was officially adopted after the government's establishment in 1912. The name "China" is derived from the Qin Dynasty (pronounced Chin).
The Chinese Dynasties
The land that is now China was inhabited by Homo erectus more than one million years ago. This is known as the Paleolithic Age (Old Stone Age), marked by the development of the first stone tools. It covers roughly 99% of human technological history. The following Neolithic Age (or New Stone Age, which is the last period of the Stone Age) can be traced back as early as 10,000 BC. With agriculture came increased population.
The first dynasty appeared around 2,100 BC. A dynasty is a succession of rulers who belong to the same family for generations. Rarely was the change of dynasties neat and clean (as the table below implies). In reality, new dynasties were often established before the overthrow of an existing regime, and old ones continued for a while after they had been defeated. In addition, China was divided for long periods of its history, with different regions being ruled by different groups.
For many years, the Xia Dynasty was thought to be just a myth since it only existed in oral stories. But in 1959, archaeological evidence was found. Despite this, they are not universally accepted as a true dynasty.
From the Qin to Qing Dynasty, there have been nearly 400 emperors, although not all of them are recognized as legitimate. Some declared themselves emperors and founded their own empires as a rival government to challenge the legitimacy of the existing emperor.
As the descendant and representative of Heaven on Earth, the emperor had absolute power over all matters, the sole and supreme overlord of the entire civilized world. Before the Qin Dynasty, they were more like kings.
Below are a few of the major dynasties and events:
DYNASTY
Xia
Shang
Western Zhou
Eastern Zhou (Spring & Autumn period)
Eastern Zhou (Warring States period)
Qin
|
DATES
2070 - 1600 BC
1600 - 1046 BC
1045 - 771 BC
770 - 476 BC
475 - 221 BC
221 - 206 BC
|
NOTED FOR
first dynasty
writing, bronze
iron
age of philosophers
expansion
first emperor, Great Wall, terracotta warriors, currency, end of human sacrifices
|
Han
Three Kingdoms
Jin
Southern & Northern
Sui
Tang
5 Dynasties & 10 Kingdoms
Song (or Sung)
Yuan
Ming
Qing
Republic of China
People's Republic of China
|
206 BC - 220
220 - 280
265 - 420
420 - 588
581 - 618
618 - 907
907 - 979
960 - 1279
1271 - 1368
1368 - 1644
1644 - 1911
1911 - 1949
1949 -
|
Silk Road
spread of Buddhism
battle tactics
stirrup, age of arts
canals, granaries
porcelain
printing, binding women's feet
printing press, gunpowder
Mongol rule
Great Wall restored, Forbidden City
last emperor & dynasty
warlord era
cultural revolution
|
return

